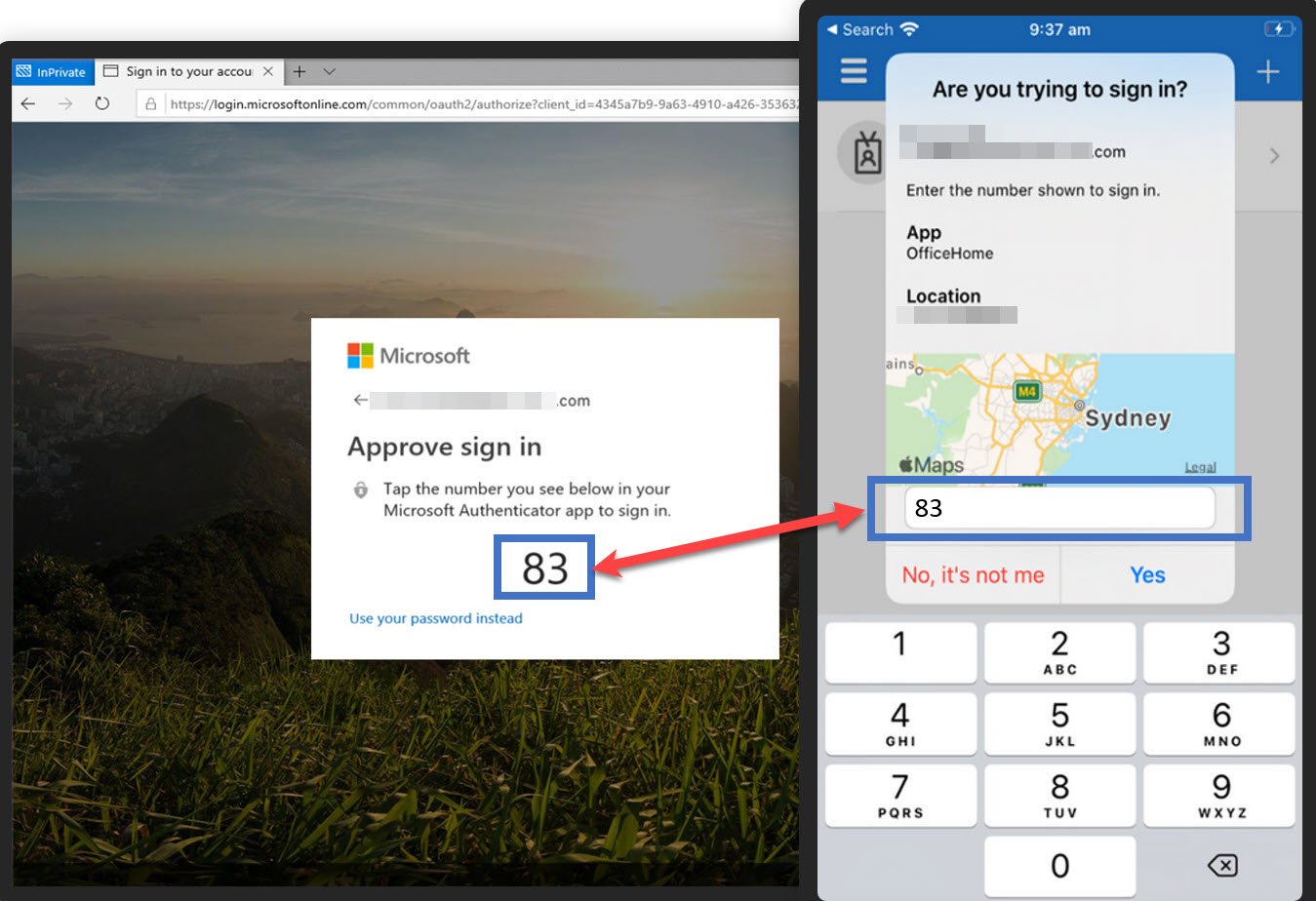
Microsoft started enforcing number matching on MFA. What does that mean for you?
Number matching in multifactor authentication push notifications typically does not refer to a common or standard authentication method. Instead, multifactor authentication (MFA) push notifications are often based on something you have (e.g., a smartphone or a dedicated hardware token) and something you know (e.g., a PIN or password).
Here's a general overview of how push notifications work in MFA with a mobile app like Microsoft Authenticator:
User Registration: The user installs the MFA mobile app (e.g., Microsoft Authenticator) on their smartphone and registers their account(s) with the app. During registration, the app generates a unique secret key that is shared with the service provider (e.g., the organization's authentication server).
Authentication Request: When the user attempts to log in to a service or application, the service provider initiates an MFA request. This request is sent to the user's registered device (typically via a push notification).
Push Notification: The MFA app on the user's smartphone receives a push notification. This notification includes details about the authentication request, such as the service or application name and a challenge.
User Approval: The user opens the MFA app and reviews the details of the authentication request to ensure it's legitimate. If the request is valid, the user approves it. This approval is often a simple action like tapping "Approve" within the app.
Confirmation: Once the user approves the request, the MFA app generates a time-based one-time password (TOTP) based on the shared secret key and the current time. This TOTP is sent back to the service provider for verification.
Verification: The service provider verifies the TOTP provided by the MFA app. If the TOTP is valid and matches the one generated by the app, the user is granted access.
The process described above does not typically involve number matching. Instead, it relies on cryptographic techniques to generate and verify TOTPs, ensuring that only the legitimate user's device can generate the correct code. This adds an additional layer of security to the authentication process beyond just a password or PIN.